ISB In the News: NIH, Viral Networks and Systems Biology
 isbscience.org/news/2014/05/14/isb-in-the-news-nih-viral-networks-and-systems-biology/
isbscience.org/news/2014/05/14/isb-in-the-news-nih-viral-networks-and-systems-biology/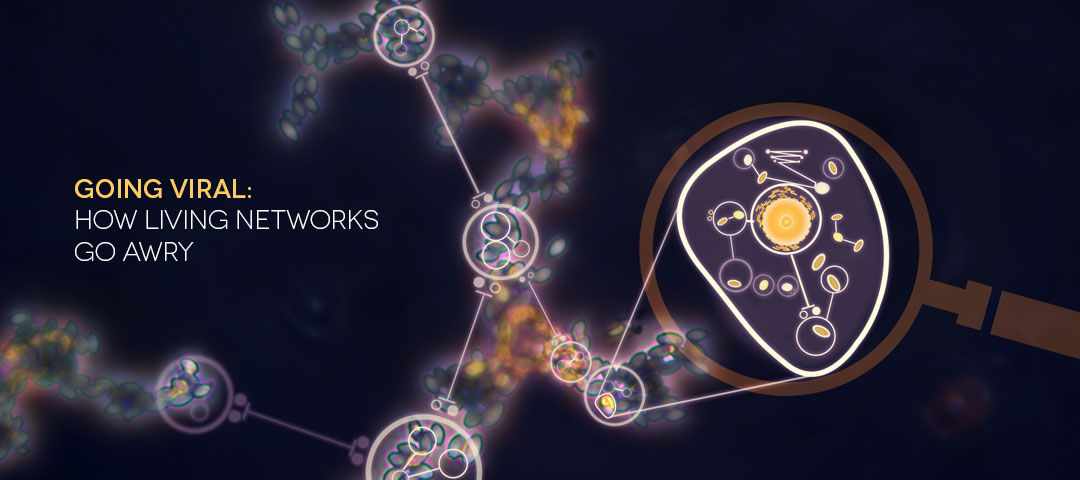
Emily Carlson and Sharon Reynolds, of the National Institutes of Health/NIGMS, posted a story on NIGMS's Inside Life Science as well as on Livescience.com on how systems biology is a powerful approach to studying biological networks. The article included comments from ISB scientist Aaron Brooks and senior research engineer Chris Lausted who created a network activity that they presented during the USA Science & Engineering Festival in Washington D.C. on April 26-27. The project was supported by funding through ISB's Center for Systems Biology and NIH/NIGMS.
"(Networks) can yield information that helps us better understand — and potentially influence — complex phenomena that affect our health."
The network diagram above — by Allison Kudla, ISB's communication designer — depicts yeast cells (superimposed circles) and the biochemical "chatter" between them (lines) that tells the cells to gather together in clumps. This clumping helps them survive stressful conditions like a shortage of nutrients.
Read the article…







