SYSTEMS BIOLOGY 101: On Being Interdisciplinary
 isbscience.org/news/2015/04/22/systems-biology-101-on-being-interdisciplinary/
isbscience.org/news/2015/04/22/systems-biology-101-on-being-interdisciplinary/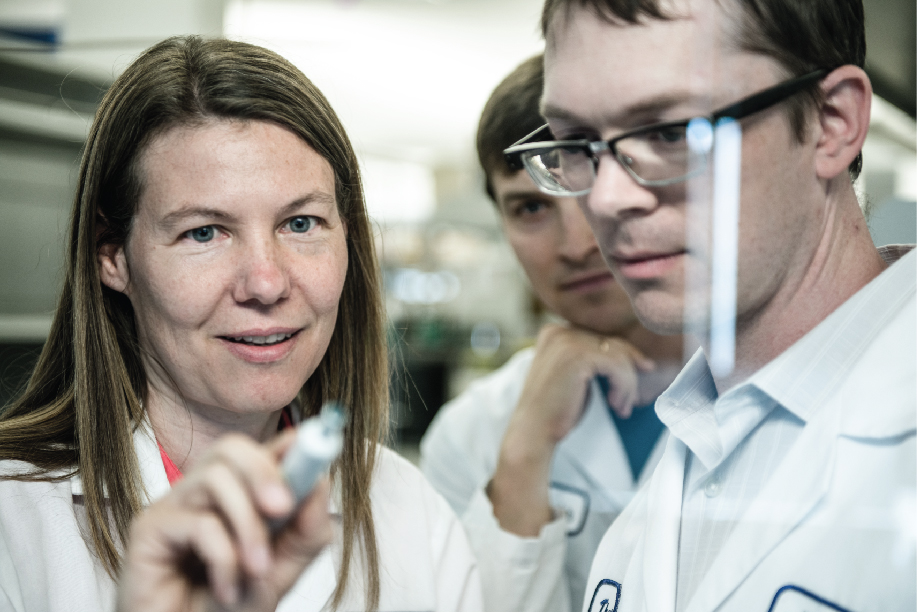
In describing systems biology and the distinguishing characteristics of ISB’s approach, we always emphasize how our lab groups are intentionally and necessarily interdisciplinary. One of our labs, for example, includes molecular biologists, microbiologists, geneticists, engineers, oceanographers, and even an astrophysicist. The complexity of biology in this age of “big data” requires diverse teams in order tackle such vast amounts of data and to make sense of it all. New technologies that crunch data faster and more efficiently also permit researchers to re-analyze existing datasets, a process which often reveals undiscovered information. Complementary skills empower any of our groups of researchers to better understand biological or environmental challenges from different perspectives and to arrive at shareable insights more quickly. Our interdisciplinary teams have contributed notable advances to everything from ocean acidification to neurodegenerative diseases and tuberculosis to multiple cancers.