ISB Recieves $1.8M Grant for Ocean Acidification Research
 isbscience.org/news/2013/06/20/isb-recieves-1-8m-grant-for-ocean-acidification-research/
isbscience.org/news/2013/06/20/isb-recieves-1-8m-grant-for-ocean-acidification-research/
Congratulations to Dr. Mónica Orellana and Dr. Nitin Baliga on their new grant for $1.8 million from the National Science Foundation. The project title is “Ocean Acidification: A Systems Biology Approach to Characterize Diatom Response to Ocean Acidification and Climate Change.”
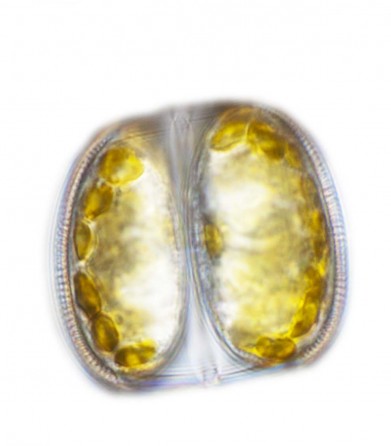
Diatom. All images of diatoms used in the promotional banner on ISB’s home page and here are courtesy of Karie Holtermann of Red Sea Research Center.
Abstract from the proposal:
Diatoms account for approximately 40 percent of primary production in the world’s oceans and are the most productive marine phytoplankton group. They form the basis of food webs in coastal and ocean upwelling areas that support important fisheries and have a major role in global carbon and silicon cycles. The goal of this project is to understand the impact of ocean acidification, in combination with other stressors, on the marine diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. This project will generate a predictive model of expression of all genes of this diatom that can be used to forecast the diatom’s response to projected environmental scenarios to an acidifying ocean. A combination of laboratory and field studies will be used; diatoms will be grown under carbon dioxide concentrations that reflect today’s values as well as future predicted conditions and light levels and nutrients concentrations will also be varied. Physiological and gene expression responses will be measured and integrated using computational and modeling methods to gain an unbiased, systems-level understanding of the response of diatoms to ocean acidification. This combined approach will enable the forecasting and prediction of the diatom’s response to environmental change and the elucidation and genomic interpretation of biochemically relevant processes in natural environment. Broader impacts: Results and the predictive model from this study can be coupled with environmental models to forecast the role and behavior of diatoms in the changing seas. In addition to the multidisciplinary training of a post-doctoral fellow and a graduate student this project will engage 3 high school teachers and their students. The investigators will continue to develop educational tools to increase the understanding of global carbon cycles by K-12 students, a generation that will be increasingly affected by the environmental changes that include ocean acidification.






